Transformation
Jun 02, 2021
Capitalising on the benefits of Artificial Intelligence of Things: Opportunities presented by AIoT

In this article, we provide examples of AIoT application across industries and explore its potential use cases and benefits.
Following the surge of AI technology advancements, the increase in demand for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, and AI chips innovation in the mid-2010s, ‘Artificial Intelligence of Things’ (AIoT) is fast emerging in the technology world and particularly in capital markets. At the same time, smart home devices, such as Google Home or Amazon Dot, are becoming increasingly popular in the consumer market.
Together with these widely available consumer products, AIoT is also being heavily utilised in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, utilities, and energy, and a large number of innovative solutions have been implemented to reduce costs, boost productivity, and improve controls and quality.
Read next: Tech trends 2021: Unprecedented challenges and opportunities
What is AIoT?
AIoT lies at the intersection of AI and IoT. The term reflects specifically the integration of software capabilities such as Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) with the infrastructure aspects of Internet of Things (IoT).
Whilst traditional IoT focuses on centralised monitoring, AIoT places further emphasis on the automation of AI-generated actionable insights. These insights can be generated locally on an edge device that has the capability to collect, analyse, and respond to sensory data.
Despite appearances, AIoT is not merely a subset of IoT. Leveraging the latest technologies from deep learning, big data, edge computing, sensor technology, and AI optimised chips, experts believe that AIoT is one of most important strategic drivers of IoT’s future.
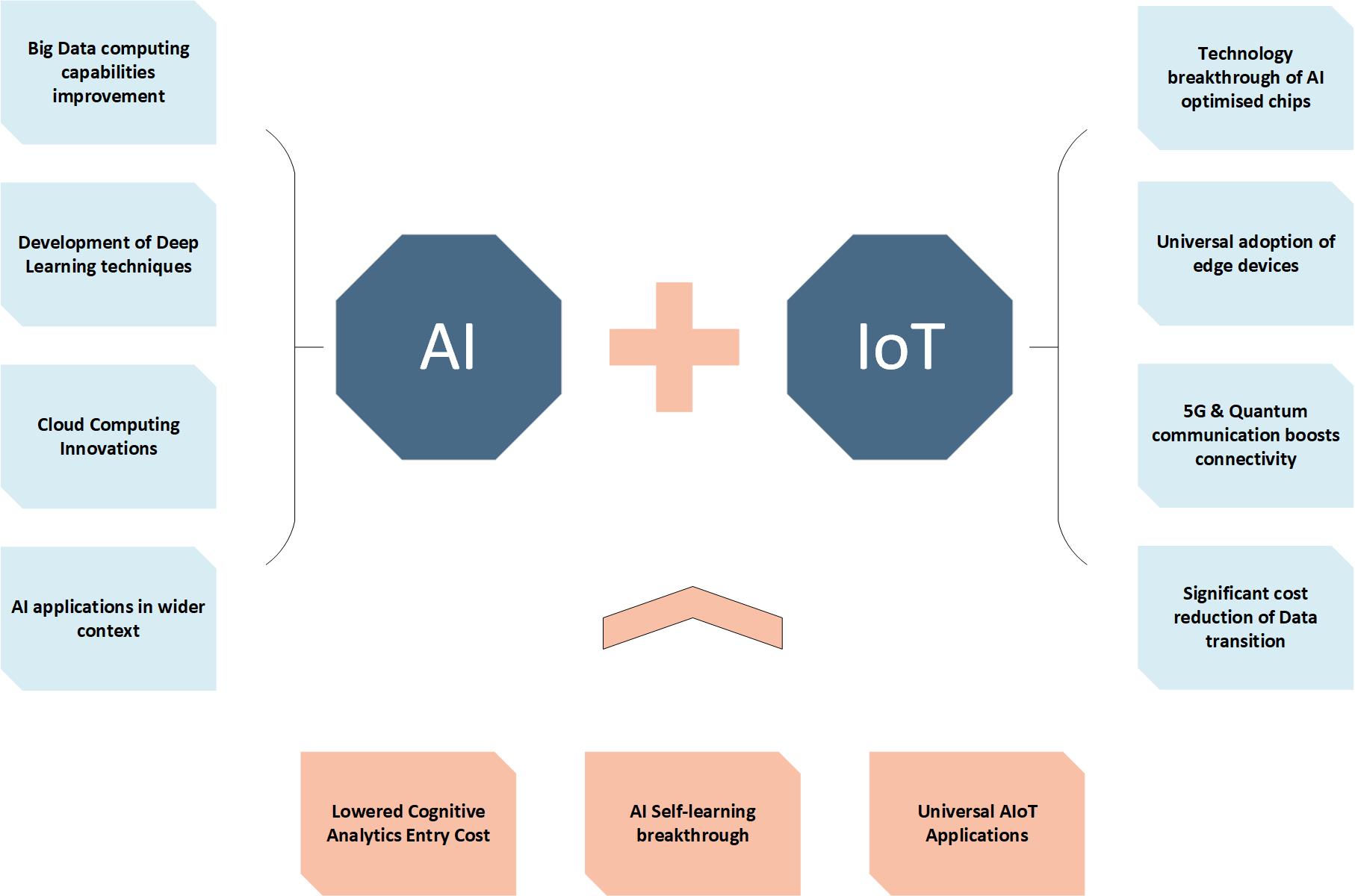
Figure 1: Key drivers to enable universal applications of AIoT’s
What are the opportunities presented by AIoT?
According to IDC, total global spending on IoT reached $742 billion in 2020, with IT and installation services and application software making up 14.2% and 11.7% respectively. Despite the impact of Covid-19 on the global economy in 2020, 47% of organisations will continue to increase their investment in IoTs, and the total market value of IoT will reach $1.12 trillion, with 30.9 billion connected devices by 2025 .
To make the UK a global centre for research and development, commercialisation, and adoption of responsible AI, the UK government has also announced a brand-new strategy that will ‘unleash the transformational power of Artificial Intelligence’. AIoT is considered one of the most important strategic applications of both IoT and AI and is expected to lead to expositional growth in the next decade.
Example use cases in industries
Taking into account the great potential for cost reduction, productivity boost, and quality improvement qualities of AIoT t, we have identified a number of simplified examples of trending use cases in an industry context.
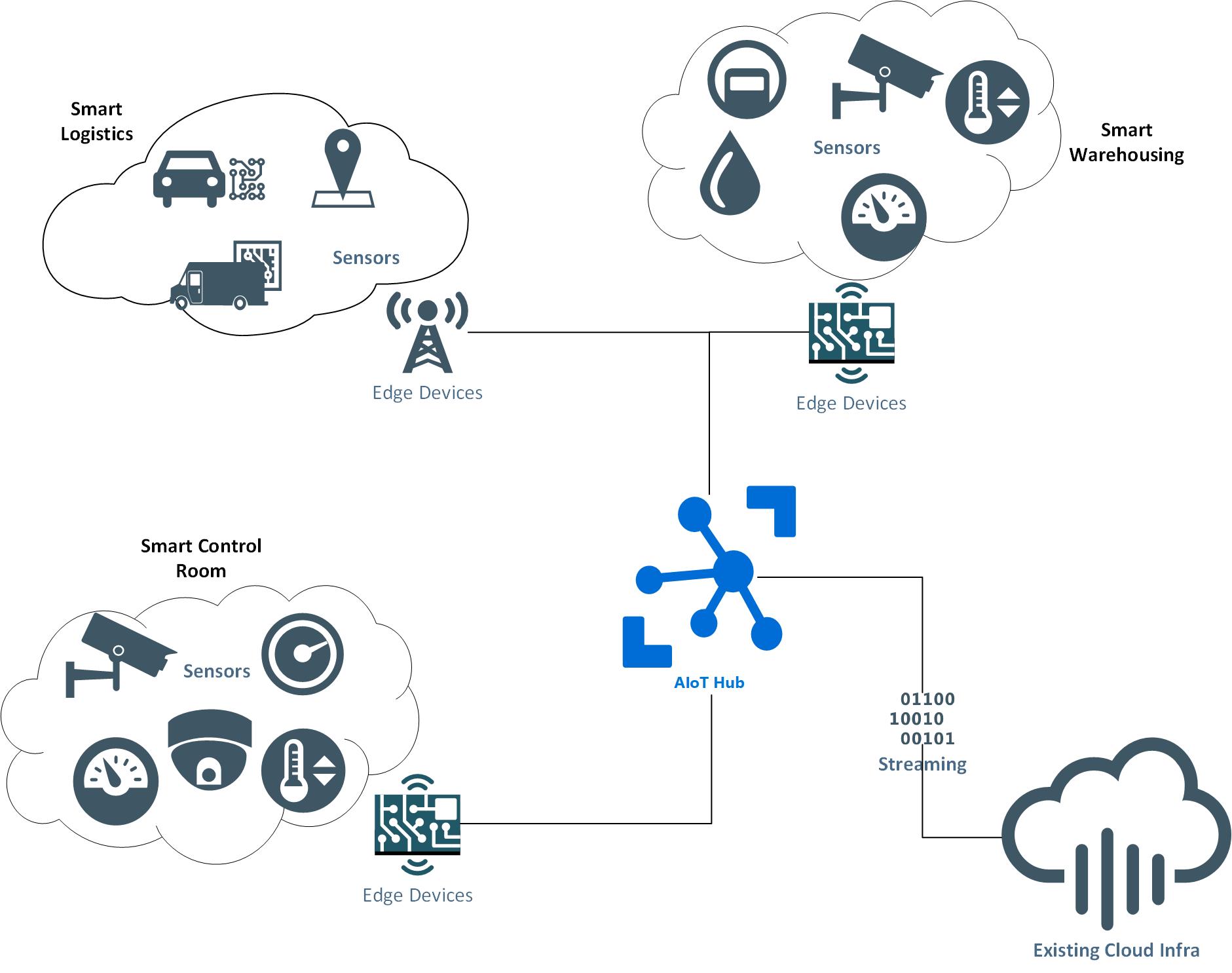
Figure 2: AIoT application in smart logistics, smart control room and smart warehousing.
Smart logistics:
Companies have previously utilised historical data with pre-set logistic schedules to manage logistic routes, vehicles, and staff. In the real world, this does not prove to be robust enough to tackle real-time variables in the logistics network.
AIoT provides a solution to these challenges because:
Edge devices installed in vehicles can communicate real-time transportation data (e.g.. routes, stops, and traffic) and vehicle status (available capacity and fuel consumption) with the centralised AI core;
Data from goods shipments (e.g. weight and dimensions, shipping costs, and driver information) AIoT can analyse the most efficient and cost-effective logistics plan and communicate instructions with drivers in real-time through edge devices.
Smart warehousing:
Thanks to the revolutionary development of computer vision technologies, compatible sensors (or cameras) can automatically identify, categorise, and monitor all stock in a warehouse. This has significantly extended the boundaries of traditional warehouse IoT solutions:
By connecting to smart logistics solutions and considering sales data, the AI core can minimise the excess stock for each type of product and automatically trigger purchase orders;
By connecting smart devices that monitor humidity, temperature, and lighting conditions, AIoT solutions can automatically advise on the best warehousing plan and trigger work orders;
In a retail warehousing context AI-enabled edge devices can detect anomalies such as product damage or food spoilage.
Smart control rooms:
Manufacturing, utilities, and energy are among some of the top industries that have deployed large numbers of IoT sensors to collect telemetry data such as machine status, process status, anomalies, or generic temperature, humidity, and pressure data. Unfortunately, the volume of IoT sensor data is often large and adds limited value. Many IoT-enabled control rooms are also facing the challenge of identifying ‘actionable insights’ from their data.
Estimates suggest that by 2025, 55.6 percent of all data will come from IoT devices, such as security cameras, RFID readers, industrial equipment, digital signage, medical implants, and other connected things.
Compared to the more traditional approaches of manually analysing sensory data and action passively, an AIoT-enabled smart control room can detect process or status anomalies in real time, and proactively recommend corrective actions.
By deploying optimised machine learning models directly to the edge devices, sensory data can be pre-processed and filtered in real-time, prior to sending to a control room for further analysis by AI models.
By adopting advanced algorithms, the centralised AI core can aid in creating targeted quality inspections towards individual artefacts, automatically orchestrating production orders and triggering maintenance procedures.
Solutions and challenges
Aside from the initial hardware investment into edge devices, the implementation of a smart AIoT solution is not as complex as it may seem.
Recent advancements in AI and machine learning techniques have transformed AIoT concepts into solutions that can be deployed at scale and pace. Thanks to the capabilities of modern cloud platforms such as Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, and Google Cloud, some barriers to accessing cutting edge AIoT technologies has also been removed.
Taking Microsoft Azure as an example, there are already a number of mature capabilities to support a fast deployment of an entry level AIoT solution:
Azure IoT Hub provides a cloud-hosted solution back end to virtually connect any compatible edge device.
Azure IoT Edge enables the deployment of cloud workloads to compatible edge devices such as machine learning models or traditional business logics.
Azure Computer Vision is part of Azure Cognitive Services, and the API uses visual data processing to analyse and label content with objects and concepts in physical spaces
Azure Anomaly Detector is part of Azure Cognitive Services, and the API can boost the reliability of business by detecting problems earlier.
By integrating AIoT Hub into any existing data streaming , event-driven IT solutions, or existing enterprise level AI cores, companies can even upgrade the entire IoT further to discover unique competitive advantages within the industry.
As with many innovations, the implementation of AIoT solutions can bring about a number of technical and process challenges, including:
Infrastructure integration of edge devices including communication protocols.
Real-time data streaming from data collection through to data processing to automated actions.
ML model optimisation to accommodate edge computing.
Adopting or evolving MLOps to tackle real-time machine learning inference.
Adapt and customise AIoT to existing operational processes.
However, considering the many advantages of matured AIoT solutions, it is clear that the benefits far outweigh the challenges.
In a nutshell
AIoT has huge potential across industries to help organisations identify and develop unique competitive advantages in the areas of operational control, quality assurance, and productivity. At the same time, the technology used to implement AIoT across industry groups is continuing to mature, whilst key challenges surrounding the selection and integration of available technologies still remain.
By partnering with Credera and leveraging the experience and knowledge of our resident AI engineers, cloud architects, data scientists, and MLOps SMEs, the route to capitalising on the benefits AIoT can be accelerated and aligned to business needs.
Contact Us
Let's talk!
We're ready to help turn your biggest challenges into your biggest advantages.
Searching for a new career?
View job openings